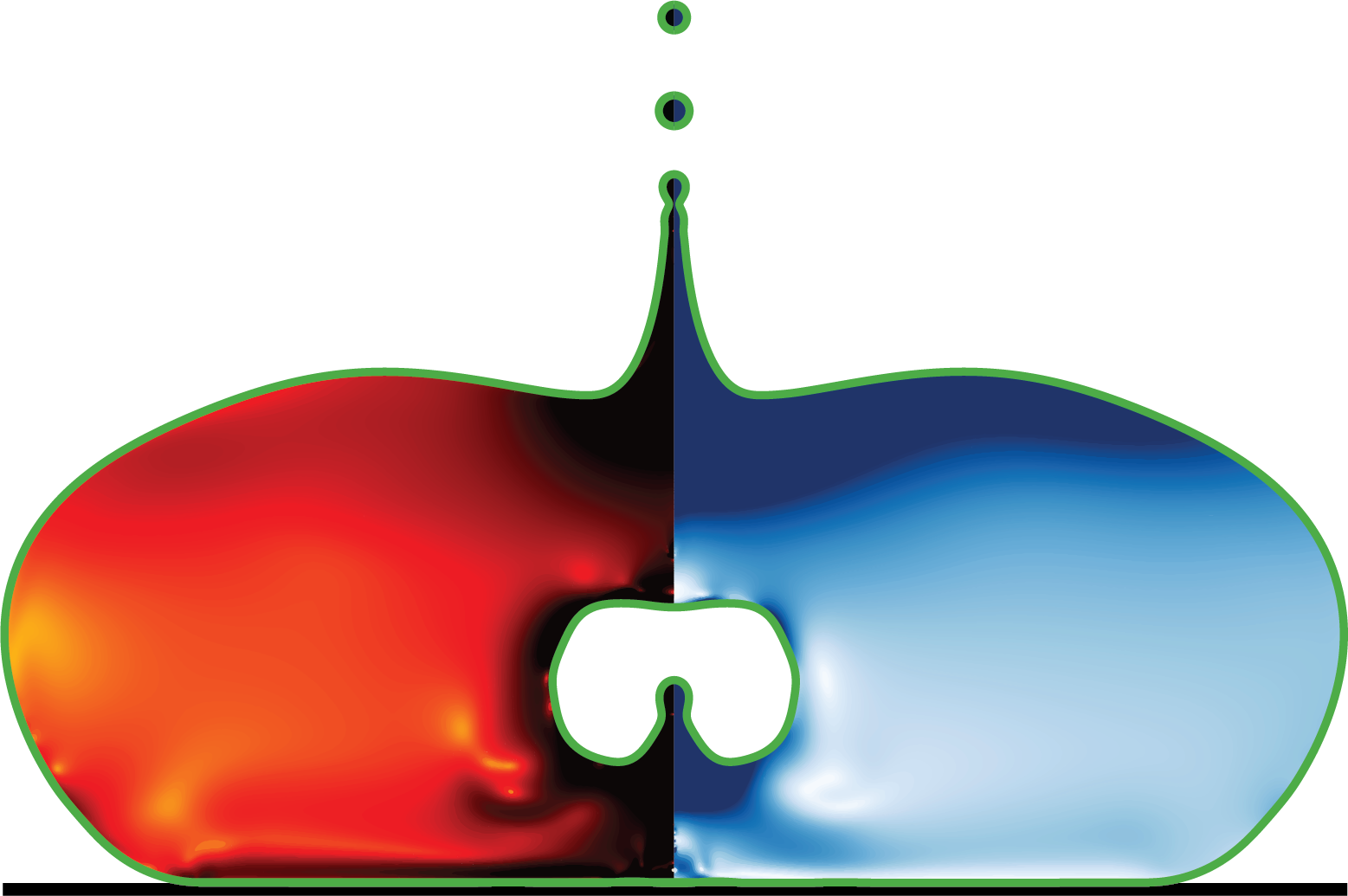
simulationCases/JumpingBubbles-hydrophilic.c
Jumping Bubbles Simulation
Overview
This code simulates the coalescence and subsequent jumping of two bubbles sitting on a hydrophilic substrate using the Basilisk C framework. The simulation employs an adaptive octree grid for spatial discretization and models two-phase flow with surface tension effects.
Physics Description
The simulation captures the dynamics of bubble coalescence-induced jumping, a phenomenon where two bubbles merge and the resulting bubble jumps away from the substrate due to the conversion of surface energy into kinetic energy. The Volume-of-Fluid (VOF) method tracks the gas-liquid interface evolution throughout the process.
Key Features
- Adaptive mesh refinement based on interface location and flow gradients
- Two-phase flow modeling with large density and viscosity contrasts
- Surface tension effects via the Continuum Surface Force (CSF) method
- STL file input for complex initial bubble geometries
Simulation Parameters
Dimensionless Numbers
Oh: Ohnesorge number - ratio of viscous to inertial-capillary forces- Controls the damping of interface oscillations
- Default: 0.01
Grid Parameters
MAXlevel: Maximum refinement level- Determines the finest grid resolution (2^MAXlevel cells)
- Default: 9
MINlevel: Minimum refinement level- Controls the coarsest grid resolution
- Fixed at: 2
Temporal Parameters
tmax: Maximum simulation time- Default: 1e-2 (MPI disabled) or 2.0 (MPI enabled)
tsnap: Time interval between solution snapshots- Fixed at: 1e-2
tsnap2: Time interval for log file outputs- Fixed at: 1e-4
Physical Parameters
Ldomain: Length of the cubic simulation domain- Fixed at: 4
Rho21: Density ratio (gas/liquid)- Fixed at: 1e-3
Mu21: Viscosity ratio (gas/liquid)- Fixed at: 1e-3
Refinement Tolerances
fErr: Interface (VOF) refinement tolerance- Fixed at: 1e-3
KErr: Curvature refinement tolerance- Fixed at: 1e-4
VelErr: Velocity field refinement tolerance- Fixed at: 1e-4
Boundary Conditions
Bottom Boundary (Substrate)
- No-slip condition: tangential and radial velocities set to zero
- Wetting condition: interface fraction f = 1 (liquid phase)
Implementation Details
Solver Configuration
- Base solver:
navier-stokes/centeredfor momentum conservation - Two-phase model: Handles density and viscosity jumps
- Surface tension: Implemented via
tension.hmodule - Conservation: Uses
navier-stokes/conserving.hfor mass conservation
Geometric Processing
distance(): Computes signed distance from STL geometryfractions(): Constructs VOF field from distance function
Compilation and Execution
Example Compilation
qcc -O2 -Wall -disable-dimensions -fopenmp JumpingBubbles.c \
-o JumpingBubbles -lmExecution
./JumpingBubblesOutput Files
dumpFile: Restart file for continuing simulationsintermediate/snapshot-*.dump: Solution snapshots at regular intervalslog: Kinetic energy evolution data
Author Information
- Author: Vatsal
- Version: 1.0
- Date: January 4, 2025
#include "grid/octree.h"
#include "navier-stokes/centered.h"
#define FILTERED 1
105
#include "two-phase.h"
#include "navier-stokes/conserving.h"
#include "tension.h"
#if !_MPI
#include "distance.h"
#endif
#define MINlevel 2
114
#define tsnap (1e-2)
115
#define tsnap2 (1e-4)
116
#define fErr (1e-3)
117
#define KErr (1e-4)
118
#define VelErr (1e-4)
119
#define Mu21 (1.00e-3)
120
#define Rho21 (1.00e-3)
121
#define Ldomain 4
122
// Boundary conditions
u.t[bottom] = dirichlet(0.);
u.r[bottom] = dirichlet(0.);
uf.t[bottom] = dirichlet(0.);
uf.r[bottom] = dirichlet(0.);
f[bottom] = dirichlet(1.);
double tmax, Oh;
int MAXlevel;
char nameOut[80], dumpFile[80];Main Function
Initializes simulation parameters and executes the run. The function sets different maximum times based on whether MPI is enabled, configures the Ohnesorge number and grid parameters, and initializes the computational domain.
Key Operations
- Sets simulation duration based on parallelization mode
- Configures physical parameters (Oh number, refinement levels)
- Initializes the grid with minimum refinement level
- Sets fluid properties based on dimensionless parameters
- Creates output directory structure
int main() {
#if !_MPI
tmax = 1e-2;
#else
tmax = 2e0;
#endif
Oh = 0.01;
MAXlevel = 9;
init_grid(1 << MINlevel);
L0 = Ldomain;
fprintf(ferr, "tmax = %g. Oh = %g\n", tmax, Oh);
rho1 = 1.0;
mu1 = Oh;
rho2 = Rho21;
mu2 = Mu21 * Oh;
f.sigma = 1.0;
char comm[80];
sprintf(comm, "mkdir -p intermediate");
system(comm);
sprintf(dumpFile, "restartFile");
run();
}Initialization Event
Sets up the initial bubble configuration either by restoring from a previous simulation or by reading an STL file containing the bubble geometry.
Workflow
- Attempts to restore from a dump file if available
- If restoration fails, reads bubble geometry from STL file
- Computes signed distance function from STL geometry
- Performs initial adaptive refinement based on distance field
- Converts distance function to VOF field using fractions()
- Initializes velocity field to zero
STL Processing Details
- Reads “InitialCondition.stl” file
- Computes bounding box of geometry
- Centers domain around bubble configuration
- Applies small vertical offset (-0.025) for substrate contact
Error Handling
- Reports if dump file restoration fails
- Exits with error if STL file is not found
- Logs bounding box coordinates for verification
event init(t = 0) {
#if _MPI
if (!restore(file = dumpFile)) {
fprintf(ferr, "Cannot restored from a dump file!\n");
}
#else
if (!restore(file = dumpFile)) {
char filename[60];
sprintf(filename, "InitialCondition.stl");
FILE * fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL) {
fprintf(ferr, "There is no file named %s\n", filename);
return 1;
}
coord * p = input_stl(fp);
fclose(fp);
coord min, max;
bounding_box(p, &min, &max);
fprintf(ferr, "xmin %g xmax %g\nymin %g ymax %g\nzmin %g zmax %g\n",
min.x, max.x, min.y, max.y, min.z, max.z);
fprintf(ferr, "x0 = %g, y0 = %g, z0 = %g\n",
0., -1.0, (min.z + max.z) / 2.);
origin(0., -1.0 - 0.025, (min.z + max.z) / 2.);
scalar d[];
distance(d, p);
while (adapt_wavelet((scalar *){f, d},
(double[]){1e-6, 1e-6 * L0},
MAXlevel).nf);
vertex scalar phi[];
foreach_vertex() {
phi[] = -(d[] + d[-1] + d[0,-1] + d[-1,-1] +
d[0,0,-1] + d[-1,0,-1] + d[0,-1,-1] + d[-1,-1,-1]) / 8.;
}
fractions(phi, f);
foreach() {
foreach_dimension() {
u.x[] = 0.0;
}
}
dump(file = "dumpInit");
fprintf(ferr, "Done with initial condition!\n");
}
#endif
}Adaptive Refinement Event
Performs dynamic mesh refinement at each timestep based on solution gradients. This ensures computational resources are concentrated in regions of high activity while maintaining accuracy.
Refinement Criteria
- Interface location (VOF field f)
- Interface curvature (computed from VOF field)
- Velocity components (all three directions)
Implementation
- Computes local curvature using the curvature() function
- Applies wavelet-based error estimation
- Refines/coarsens cells based on error tolerances
- Maintains refinement between MINlevel and MAXlevel
event adapt(i++) {
scalar KAPPA[];
curvature(f, KAPPA);
adapt_wavelet((scalar *){f, KAPPA, u.x, u.y, u.z},
(double[]){fErr, KErr, VelErr, VelErr, VelErr},
MAXlevel, MINlevel);
}File Output Event
Writes solution snapshots at regular intervals for post-processing and visualization. Creates both restart files and timestamped snapshots.
Output Schedule
- Triggers at t = 0 and every tsnap interval
- Continues until tmax + tsnap
File Structure
- Overwrites main restart file at each output
- Creates timestamped snapshots in intermediate/ directory
- Uses 5.4f format for time in filenames
event writingFiles(t = 0; t += tsnap; t <= tmax + tsnap) {
dump(file = dumpFile);
char nameOut[80];
sprintf(nameOut, "intermediate/snapshot-%5.4f", t);
dump(file = nameOut);
}Logging Event
Records integral quantities at high frequency for quantitative analysis. Specifically tracks the kinetic energy of the gas phase to monitor bubble dynamics.
Computed Quantities
- Kinetic energy of gas phase: KE = 0.5 * ρ * (u² + v² + w²) * (1-f) * ΔV
- Uses clamp() to ensure clean phase separation
Output Format
- Headers: i (iteration), dt (timestep), t (time), ke (kinetic energy)
- Writes to both stderr and “log” file
- Appends to existing log file after initial write
Parallel Considerations
- Uses reduction operation for parallel summation
- Only process 0 performs file I/O
event logWriting(t = 0; t += tsnap2; t <= tmax + tsnap) {
double ke = 0.;
foreach(reduction(+:ke)) {
ke += 0.5 * (sq(u.x[]) + sq(u.y[]) + sq(u.z[])) *
clamp(1. - f[], 0., 1.) * cube(Delta);
}
if (pid() == 0) {
static FILE * fp;
if (i == 0) {
fprintf(ferr, "i dt t ke\n");
fp = fopen("log", "w");
fprintf(fp, "i dt t ke\n");
fprintf(fp, "%d %g %g %g\n", i, dt, t, ke);
fclose(fp);
} else {
fp = fopen("log", "a");
fprintf(fp, "%d %g %g %g\n", i, dt, t, ke);
fclose(fp);
}
fprintf(ferr, "%d %g %g %g\n", i, dt, t, ke);
}
}