ElastoFlow: 2D/3D Viscoelastic Fluid Simulation Framework
🚀 ElastoFlow is a state-of-the-art, open-source framework for simulating viscoelastic fluid flows in 2D and 3D, built as an extension to the Basilisk C CFD library. It implements the log-conformation method for robust, high-Weissenberg number simulations, with a focus on clarity, extensibility, and scientific rigor.
✨ Key Features
- Full 3D Log-Conformation Method: Complete scalar implementation for 3D viscoelastic fluids (log-conform-viscoelastic-scalar-3D.h)
- Robust 2D/Axi Support: Scalar and tensor-based log-conformation for 2D and axisymmetric cases (log-conform-viscoelastic-scalar-2D.h, log-conform-viscoelastic.h)
- Optimized Matrix Algebra: Efficient, stable eigenvalue and tensor operations (eigen_decomposition.h)
- Advanced Initialization: Functions for pseudo vectors/tensors in 2D/3D
- Error Handling: Negative eigenvalue checks, eigenvalue clamping, and detailed diagnostics
- Performance: Simplified acceleration term calculations and optimized tensor operations
- Documentation: Extensive inline documentation, mathematical background, and verification notes
- Compatibility: GPLv3 license, fully compatible with Basilisk and previous ElastoFlow versions
🐛 Bug Fixes (v2.5/v2.6)
- Corrected matrix algebra in 3D
- Fixed rotation tensor and eigenvalue edge cases
- Improved error reporting and diagnostics
- Enhanced axisymmetric and 2D/3D compatibility
🗂️ Repository Structure
- basilisk/src/ - # Core Basilisk CFD library (reference only, do not modify)
- src-local/
- # Custom viscoelastic solvers and tensor utilities
- log-conform-viscoelastic-scalar-3D.h - # 3D log-conformation (scalar)
- log-conform-viscoelastic-scalar-2D.h - # 2D/axi log-conformation (scalar)
- log-conform-viscoelastic.h - # 2D/axi log-conformation (tensor)
- two-phaseVE.h - # Two-phase viscoelastic extension
- eigen_decomposition.h - # 3x3 symmetric eigenvalue solver
- simulationCases/ - #
Example/test cases and post-processing scripts
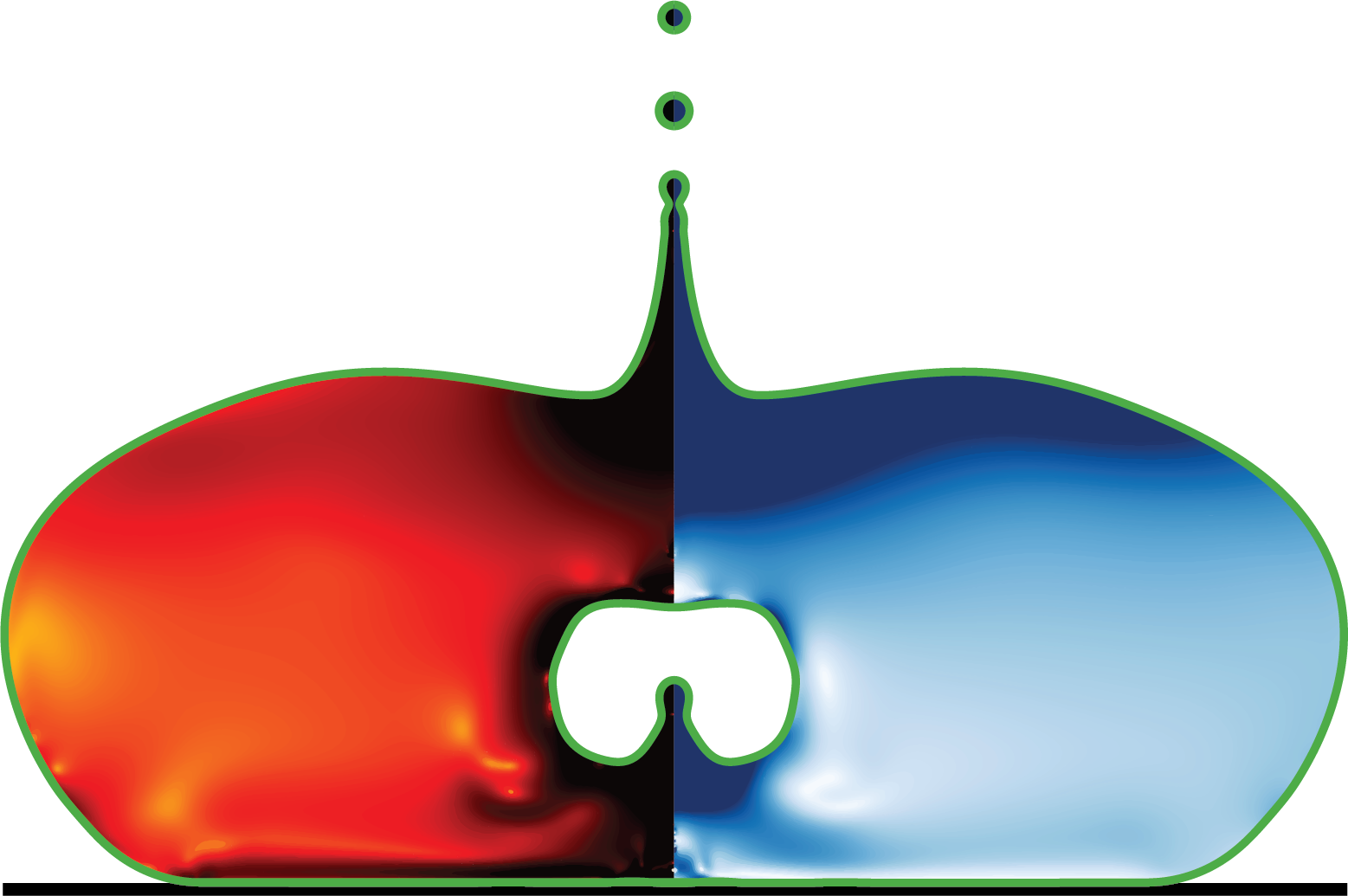
- dropAtomisation.c - # 3D drop atomisation simulation
- pinchOff.c - # Pinch-off of viscoelastic jet (2D/axi)
- testEigenDecomposition.c - # Eigenvalue solver test/verification
- dropImpact.c - # Drop impact simulation
- verifyWtihPlots.ipynb - # Jupyter notebook for verification/plots
- postProcess/ - #
Project-specific post-processing tools and utilities
- getData-elastic-scalar2D.c - # Data extraction utility
- getFacet2D.c - # Facet extraction utility
- VideoAxi.py - # Python visualization script
📚 Documentation
- docs/ — Full HTML documentation, mathematical background, and API
- Inline documentation in all major headers (see
src-local/) - Example simulation and post-processing scripts in
simulationCases/
🚀 Quick Start
1. Prerequisites
- Basilisk C
(included as submodule in
basilisk/) - C compiler (e.g., gcc)
- Python 3 (for post-processing)
- Optional: Jupyter for notebooks
2. Compiling & Running Simulations
A. Vanilla Basilisk method:
qcc -O2 -Wall -I./src-local -disable-dimensions simulationCases/{CaseName}.c -o {CaseName} -lm
./{CaseName}B. Using the Makefile (with bview browser):
CFLAGS=-DDISPLAY=-1 make simulationCases/{CaseName}.tst- For interactive visualization, open the generated
display.htmlin your browser (see Basilisk bview).
3. Post-Processing & Analysis
- Python scripts and Jupyter notebooks for data
extraction and visualization are in
simulationCases/(e.g.,VideoAxi.py,verifyWtihPlots.ipynb). - Example utilities:
getData-elastic-scalar2D.c,getFacet2D.c.
📝 Example: Running a 3D Drop Atomisation Simulation
qcc -O2 -Wall -I./src-local -disable-dimensions simulationCases/dropAtomisation.c -o dropAtomisation -lm
./dropAtomisation🔍 Technical Details
- Log-Conformation Method: See src-local/log-conform-viscoelastic-scalar-3D.h and src-local/log-conform-viscoelastic-scalar-2D.h for mathematical background and implementation notes.
- Eigenvalue Solver: src-local/eigen_decomposition.h provides robust 3x3 symmetric eigensystem routines.
- Two-Phase Flows: src-local/two-phaseVE.h extends Basilisk’s two-phase solver for viscoelasticity.
- Axisymmetric/2D/3D: Use the appropriate header for your geometry (see comments in each header for guidance).
🧑💻 Contributing
- See CLAUDE.md for code style and development guidelines.
- Issue templates and feature requests: GitHub Issue Templates
- Pull requests are welcome! Please document your changes and update relevant tests/examples.
📋 License
This project is licensed under the GNU GPLv3, in line with the Basilisk codebase.
🙏 Acknowledgments
- Thanks to all contributors and the Basilisk community
🔗 References
- Fattal & Kupferman (2004, 2005): Log-conformation method
- Comminal et al. (2015): Constitutive model functions
- Hao & Pan (2007): Split scheme implementation
- Basilisk C
For detailed documentation, see the docs/ folder or open
docs/index.html in your browser.
Generated Documentation
Root Directory
postProcess
simulationCases
- simulationCases/dropAtomisation.c
- simulationCases/dropImpact.c
- simulationCases/pinchOff.c
- simulationCases/testEigenDecomposition.c
- simulationCases/verifyWtihPlots.ipynb