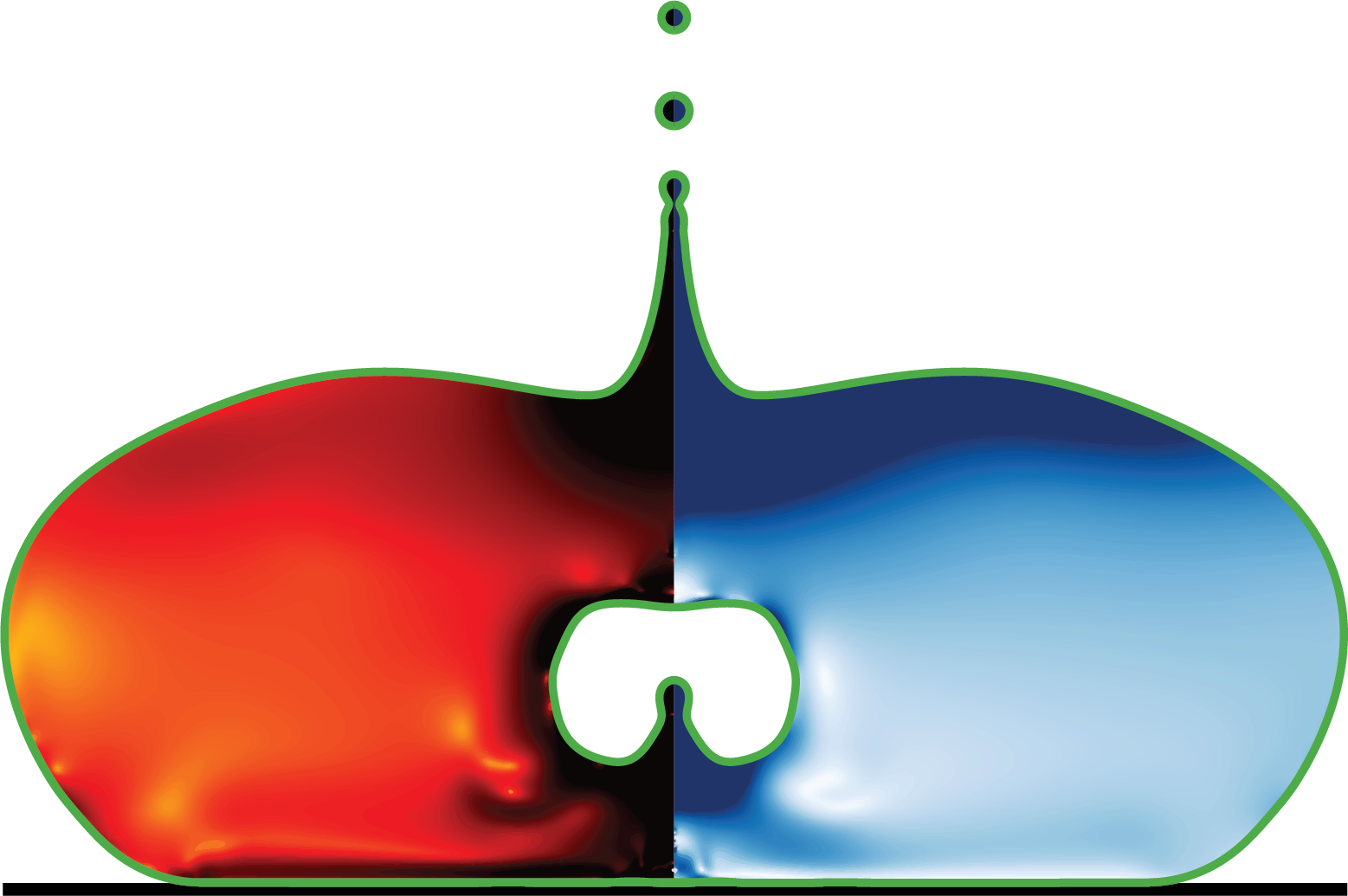
simulationCases/pinchOff.c
Viscoelastic Liquid Jet Pinch-Off Simulation
This file implements an axisymmetric simulation of the pinch-off dynamics of a viscoelastic liquid jet. The simulation uses a two-phase approach with log-conformation formulation for the viscoelastic stress tensor.
The model incorporates: - Axisymmetric Navier-Stokes equations - Log-conformation viscoelastic constitutive model - Two-phase interface with surface tension - Adaptive mesh refinement based on interface curvature and velocity gradients
File Information
- File: pinchOff.c
- Version: 0.2
- Author: Vatsal Sanjay
- Date: Oct 18, 2024
#include "axi.h"
// #include "grid/octree.h"
// #include "grid/quadtree.h"
#include "navier-stokes/centered.h"
#define VANILLA 1
26
#if VANILLA
#include "../src-local/log-conform-viscoelastic.h"
#define logFile "logAxi-vanilla.dat"
29
#else
#if AXI
#include "../src-local/log-conform-viscoelastic-scalar-2D.h"
#define logFile "logAxi-scalar.dat"
33
#else
#include "../src-local/log-conform-viscoelastic-scalar-3D.h"
#define logFile "log3D-scalar.dat"
36
#endif
#endif
#define FILTERED // Smear density and viscosity jumps
#include "../src-local/two-phaseVE.h"
#include "navier-stokes/conserving.h"
#include "tension.h"## Simulation Parameters
Configuration of time steps, error tolerances, and physical parameters.
Time between snapshots
#define tsnap (1e-2)
53
54
### Error Tolerances
- fErr: Error tolerance in volume fraction field (f1 VOF)
- KErr: Error tolerance in interface curvature calculation using height function
- VelErr: Error tolerances in velocity field Use 1e-2 for low Oh (Ohnesorge number) cases Use 1e-3 to 5e-3 for high Oh/moderate to high J cases
#define fErr (1e-3)
64
#define KErr (1e-6)
65
#define VelErr (1e-2)
66
67
### Geometry Parameters
Parameters defining the initial geometry of the liquid jet
#define epsilon (0.5)
73
#define R2(x,y,z,e) (sqrt(sq(y) + sq(z)) + (e*sin(x/4.)))
74
75
## Boundary Conditions
Neumann boundary condition for velocity and Dirichlet for pressure at the top
u.n[top] = neumann(0.0);
p[top] = dirichlet(0.0);## Global Variables
- MAXlevel: Maximum level of mesh refinement
- Oh: Ohnesorge number for the liquid phase (solvent)
- Oha: Ohnesorge number for the gas phase (air)
- De: Deborah number - ratio of relaxation time to flow time
- Ec: Elasto-capillary number - ratio of elastic to capillary forces
int MAXlevel;
double Oh, Oha, De, Ec, tmax;
char nameOut[80], dumpFile[80];## Main Function
Initializes the simulation parameters and starts the simulation.
- Sets domain size
- Configures physical parameters (Oh, De, Ec)
- Initializes grid
- Sets up file storage
- Configures material properties
### Parameters - argc: Command line argument count - argv: Command line argument values
### Returns - Exit status code
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
L0 = 2*pi;
// Values taken from the terminal
MAXlevel = 6;
tmax = 10;
Oh = 1e-2;
Oha = 1e-2 * Oh;
De = 1.0; // 1e-1;
Ec = 1.0; // 1e-2;
init_grid(1 << 4);
// Create a folder named intermediate where all the simulation snapshots are stored
char comm[80];
sprintf(comm, "mkdir -p intermediate");
system(comm);
// Name of the restart file. See writingFiles event
sprintf(dumpFile, "restart");
// Set material properties
rho1 = 1., rho2 = 1e-3;
mu1 = Oh, mu2 = Oha;
lambda1 = De, lambda2 = 0.;
G1 = Ec, G2 = 0.;
f.sigma = 1.0;
run();
}## Initialization Event
Sets up the initial condition for the simulation.
- Attempts to restore from a restart file if available
- Otherwise initializes the interface using the geometric function
- Refines the mesh around the interface
### Parameters - t: Simulation time (starts at 0)
event init(t = 0) {
if (!restore(file = dumpFile)) {
refine(R2(x,y,z,epsilon) < (1+epsilon) && R2(x,y,z,epsilon) > (1-epsilon)
&& level < MAXlevel);
fraction(f, (1-R2(x,y,z,epsilon)));
}
}## Adaptive Mesh Refinement
Dynamically adjusts the mesh resolution based on interface curvature and flow features.
- Calculates interface curvature
- Refines mesh based on error criteria for volume fraction, velocity, and curvature fields
### Parameters - i: Iteration number
event adapt(i++) {
scalar KAPPA[];
curvature(f, KAPPA);
adapt_wavelet((scalar *){f, u.x, u.y, KAPPA},
(double[]){fErr, VelErr, VelErr, KErr},
MAXlevel, 4);
}## Snapshot Generation
Saves the state of the simulation at regular intervals.
- Creates a restart file for potential simulation recovery
- Generates a snapshot file with timestamped name
### Parameters - t: Simulation time (starts at 0, incremented by tsnap until tmax)
event writingFiles(t = 0; t += tsnap; t <= tmax) {
dump(file = dumpFile);
sprintf(nameOut, "intermediate/snapshot-%5.4f", t);
dump(file = nameOut);
}## Simulation Termination
Outputs final information when the simulation ends.
- Prints the maximum refinement level and Ohnesorge number
### Parameters - t: Simulation time (at end)
event end(t = end) {
if (pid() == 0)
fprintf(ferr, "Level %d, Oh %2.1e\n", MAXlevel, Oh);
}## Data Logging
Records simulation statistics at each iteration.
- Calculates total kinetic energy
- Identifies the minimum position of the interface along the y-axis
- Writes data to the log file
- Checks for simulation stability based on kinetic energy
### Parameters - i: Iteration number
### Notes - Terminates the simulation if kinetic energy is too high (blow-up) or too low - Creates a final restart file if the simulation is terminated early
event logWriting(i++) {
// Calculate kinetic energy
double ke = 0.;
foreach (reduction(+:ke)) {
ke += (2*pi*y)*(0.5*rho(f[])*(sq(u.x[]) + sq(u.y[])+ sq(u.z[])))*sq(Delta);
}
static FILE * fp;
if (pid() == 0) {
const char* mode = (i == 0) ? "w" : "a";
fp = fopen(logFile, mode);
if (fp == NULL) {
fprintf(ferr, "Error opening log file\n");
return 1;
}
// Find minimum position of interface along y-axis
scalar pos[];
position(f, pos, {0,1,0});
double ymin = statsf(pos).min;
// Write header for first iteration
if (i == 0) {
fprintf(ferr, "Level %d, Oh %2.1e, Oha %2.1e, De %2.1e, Ec %2.1e\n",
MAXlevel, Oh, Oha, De, Ec);
fprintf(ferr, "i dt t ke ymin\n");
fprintf(fp, "Level %d, Oh %2.1e, Oha %2.1e, De %2.1e, Ec %2.1e\n",
MAXlevel, Oh, Oha, De, Ec);
fprintf(fp, "i dt t ke ymin\n");
}
// Write data row
fprintf(fp, "%d %g %g %g %g\n", i, dt, t, ke, ymin);
fprintf(ferr, "%d %g %g %g %g\n", i, dt, t, ke, ymin);
fflush(fp);
fclose(fp);
}
// Check for negative kinetic energy (should never happen)
assert(ke > -1e-10);
// Check for simulation stability after a few iterations
if (i > 1e1 && pid() == 0) {
if (ke > 1e2 || ke < 1e-8) {
const char* message = (ke > 1e2) ?
"The kinetic energy blew up. Stopping simulation\n" :
"kinetic energy too small now! Stopping!\n";
fprintf(ferr, "%s", message);
fp = fopen("log", "a");
fprintf(fp, "%s", message);
fflush(fp);
fclose(fp);
dump(file = dumpFile);
return 1;
}
}
}